An effective identity security program requires the collaboration of various stakeholders, each with their own roles and responsibilities. These stakeholders play a crucial role in ensuring the program's successful implementation and mitigating the risks associated with identity-related vulnerabilities. In this blog, we will discuss the key stakeholders involved in an identity security program and explore their roles and responsibilities.
The Usual Suspects
The following personas typically have a hand in driving or supporting identity security. That said, all organizations are unique in their organizational structure and size. Adapt these roles to your team to understand who should be responsible, accountable, supporting, consulting and informed as you build your program and team
End Users
End-users, including employees and partners, are the individuals who use the organization's information systems. Their primary objectives are to have safe and secure access to information, protect personal data, and prevent unauthorized access to confidential information. End-users are responsible for following best practices for password management, promptly reporting any suspicious activity, and complying with the organization's security policies. By focusing on the needs of end-users, other stakeholders, such as the security and IT teams, can work together more effectively.
CISO (Chief Information Security Officer)
The CISO holds a critical role in overseeing the organization's security program and ensuring that it aligns with the organization's business objectives. Their primary goals include minimizing the organization's risk exposure, enhancing its security posture, and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. The CISO is responsible for setting security strategies, communicating security risks to executive leadership, and providing guidance to the security teams.
Security Team
The security team is responsible for monitoring the organization's security posture, identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities, and responding to security incidents. They aim to identify and mitigate risks, prevent data breaches, and minimize the impact of security incidents. The security team's responsibilities include performing regular security assessments, implementing incident response plans, and monitoring security logs.
Cyber Threat Intelligence Team
The Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) team tracks and analyzes threats to the organization, focusing on understanding the potential impact to the business. Their desired outcome is to protect the organization against common attacker techniques. The CTI team's responsibilities include providing assessments on new identity-based techniques, identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) from recent campaigns, and detecting breached credentials.
IAM (Identity and Access Management) Team
The IAM team is responsible for managing user identities, access rights, and privileges within the organization. They aim to ensure that users have appropriate access to systems and data, minimize the risk of unauthorized access, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. The IAM team's responsibilities include defining access policies, managing user accounts and entitlements, and monitoring user activity.
IT Help Desk
The IT Help Desk provides technical support to end-users, specifically addressing identity and access-related issues. Their objectives include resolving issues such as password resets and account lockouts in a timely and secure manner. The IT Help Desk's responsibilities include verifying users' identities before granting access, following established security procedures, and escalating security incidents to the appropriate teams.
CIO (Chief Information Officer)
The CIO is responsible for managing the organization's information technology infrastructure and ensuring its alignment with the business goals. Their desired outcomes include aligning IT with the organization's strategic objectives, improving IT efficiency, and managing IT costs. The CIO oversees the implementation of the identity security program, ensuring that it meets the organization's security and regulatory requirements, and providing necessary resources to support the program.
Compliance Team
The compliance team is responsible for ensuring that the organization complies with applicable regulatory requirements and industry standards. Their goals include maintaining compliance, avoiding penalties, and enhancing the organization's reputation. The compliance team's responsibilities encompass assessing compliance requirements, implementing controls to meet those requirements, and reporting on compliance status.
Responsibilities for Identity Security: RASCI Example
To illustrate the responsibilities of the key stakeholders, a RASCI (Responsible, Accountable, Supporting, Consulted, Informed) matrix can be utilized. While each organization's structure may differ, a typical example includes the IAM team reporting to the CIO and the security team reporting to the CISO. The specific responsibilities of the CIO and CISO may vary depending on the organization.
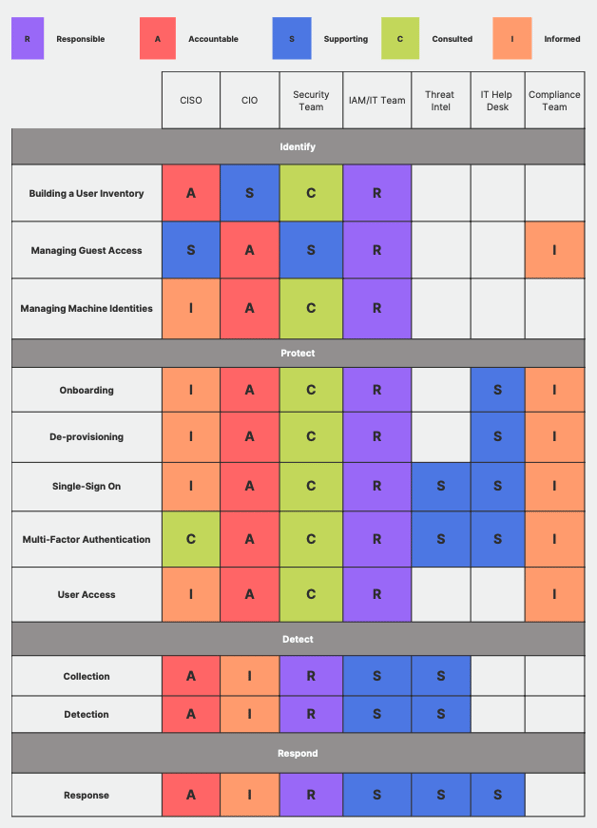 Source: Building an Identity Security Program - A Blueprint, Oort 2023
Source: Building an Identity Security Program - A Blueprint, Oort 2023
Conclusion
In an identity security program, collaboration among various stakeholders is crucial for its success. Each stakeholder has distinct roles and responsibilities that contribute to the overall protection of the organization's digital identities. By recognizing the importance of these stakeholders and their respective responsibilities, organizations can build a robust identity security framework and effectively mitigate the risks associated with identity-related threats.
Getting the right team involved is critical to success as you build your identity security program. We have built a comprehensive blueprint for building an identity security program that begins with understanding your current maturity across 11 factors. Download the full guide and contact us if you have any questions.
Oort’s Identity Security Platform
Oort is an identity-centric enterprise security platform. As a turnkey solution for Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR), Oort is providing immediate value to security teams by working with existing sources of identity to enable comprehensive identity attack surface management in minutes. Led by a team with decades of domain expertise across identity, networking, and security, Oort is backed by venture capital investors including Energy Impact Partners, .406 Ventures, Bain Capital Ventures, Cisco Investments and others. Market-leading technology companies, like Collibra and Avid Technology, rely on Oort to provide full visibility into their identity populations.
To get a free identity security health assessment, request a demo.



